According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), developers plan to add 54.5 gigawatts (GW) of new utility-scale electric generating capacity to the U.S. power grid in 2023. More than half of this capacity will be solar. Wind power and battery storage are expected to account for roughly 11 percent and 17 percent, respectively.
A large percentage of new installations are being developed in areas that are prone to extreme weather events and natural disasters (e.g., Texas and California), including high wind, tornadoes, hail, flooding, earthquakes, wildfires, etc. With the frequency and severity of many of these events increasing, project developers, asset owners, and tax equity partners are under growing pressure to better understand and mitigate risk.
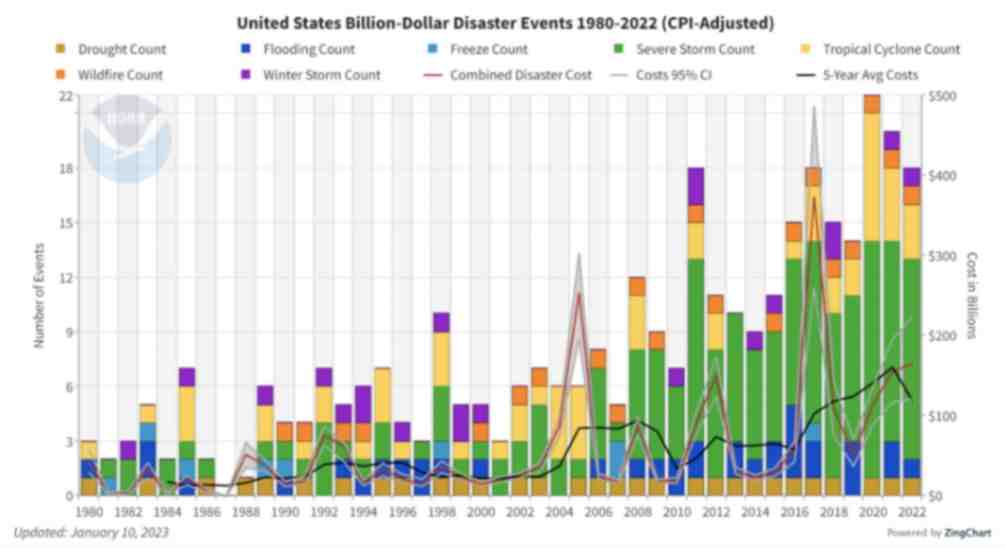
Figure 1. The history of billion-dollar disasters in the United States each year from 1980 to 2022 (source: NOAA)
In terms of loss prevention, a Catastrophe (CAT) Modeling Study is the first step to understanding the exposure and potential financial loss from natural hazards or extreme weather events. CAT studies form the foundation for wider risk management strategies, and have significant implications for insurance costs and coverage.
Despite their importance, developers often view these studies as little more than a formality required for project financing. As a result, they are often conducted late in the development cycle, typically after a site has been selected. However, a strong case can be made for engaging early with an independent third party to perform a more rigorous site-specific technical assessment. Doing so can provide several advantages over traditional assessments conducted by insurance brokerage affiliates, who may not possess the specialty expertise or technical understanding needed to properly apply models or interpret the results they generate. One notable advantage of early-stage catastrophe studies is to help ensure that the range of insurance costs, which can vary from year to year with market forces, are adequately incorporated into the project financial projections.
The evolving threat of natural disasters
Over the past decade, the financial impact of natural hazard events globally has been almost three trillion dollars. In the U.S. alone, the 10-year average annual cost of natural disaster events exceeding $1 billion increased more than fourfold between the 1980s ($18.4 billion) and the 2010s ($84.5 billion).
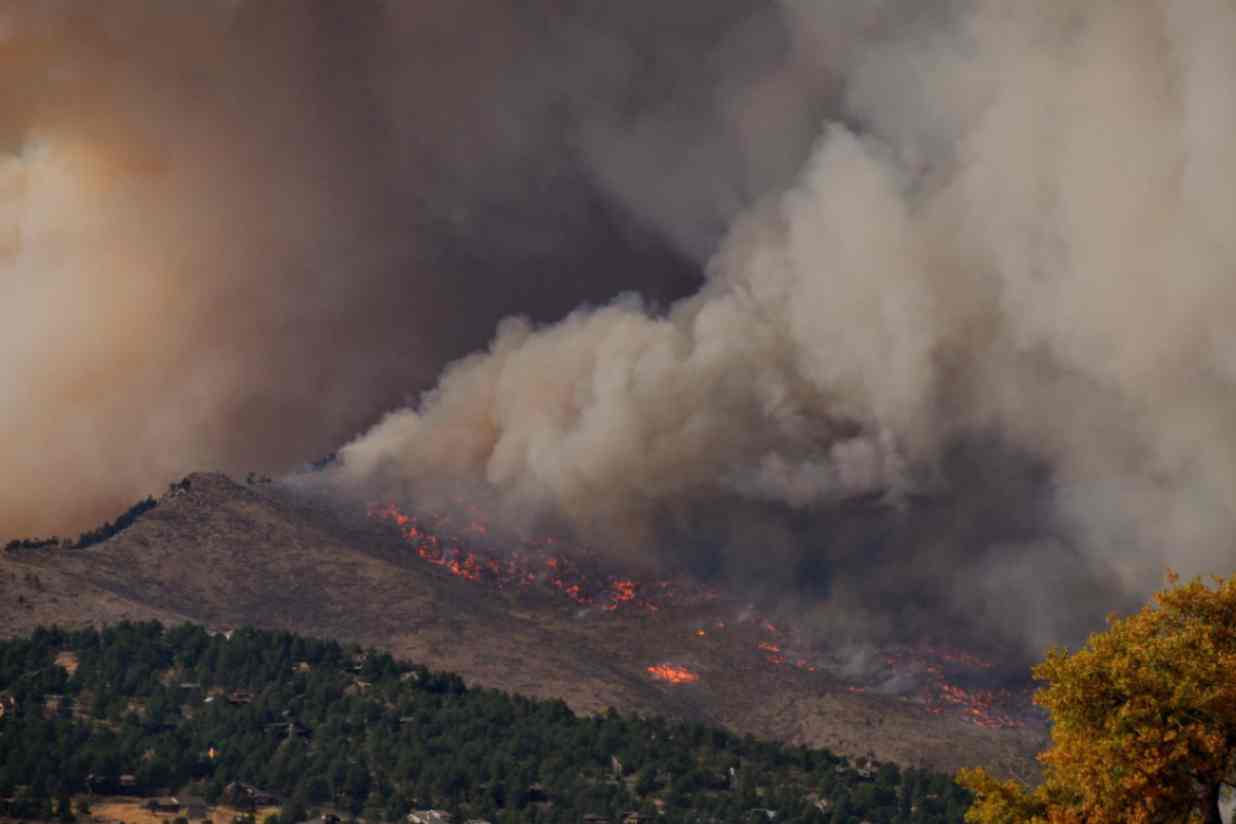

Investors, insurers, and financiers of renewable projects have taken notice of this trend, and are subsequently adapting their behavior and standards accordingly. In the solar market, for example, insurance premiums increased roughly four-fold from 2019 to 2021. The impetus for this increase can largely be traced back to a severe storm in Texas in 2019, which resulted in an $80 million loss on 13,000 solar panels that were damaged by hail.
The event awakened the industry to the hazards severe storms present, particularly when it comes to large-scale solar arrays. Since then, the impact of convective weather on existing and planned installations has been more thoroughly evaluated during the underwriting process. However, far less attention has been given to the potential for other natural disasters; events like floods and earthquakes have not yet resulted in large losses and/or claims on renewable projects (including wind farms). The extraordinary and widespread effect of the recent Canadian wildfires may alter this behavior moving forward.
A thorough assessment, starting with a CAT study, is key to quantifying the probability of their occurrence — and estimating potential losses — so that appropriate measures can be taken to mitigate risk.
All models are not created equal
Industrywide, certain misconceptions persist around the use of CAT models to estimate losses from an extreme weather event or natural disaster.
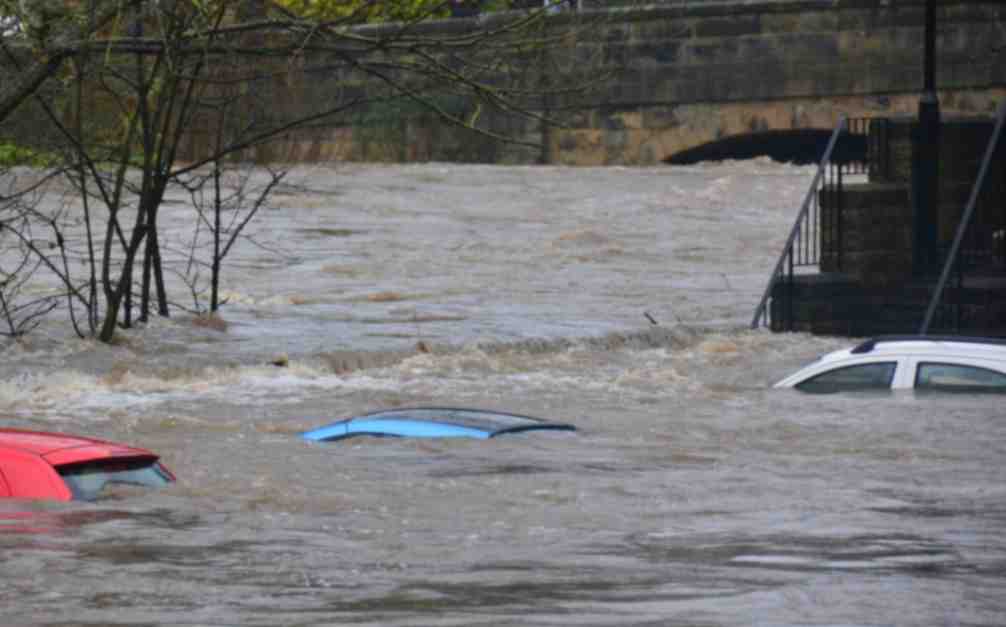

Often, the perception is that risk assessors only need a handful of model inputs to arrive at an accurate figure, with the geographic location being the most important variable. While it’s true that many practitioners running models will pre-specify certain project characteristics regardless of the asset’s design (for example, the use of steel moment frames without trackers for all solar arrays in a given region or state), failure to account for even minor details can lead to loss estimates that are off by multiple orders of magnitude.
The evaluation process has recently become even more complex with the addition of battery energy storage. Relative to standalone solar and wind farms, very little real-world experience and data on the impact of extreme weather events has been accrued on these large-scale storage installations. Such projects require an even greater level of granularity to help ensure that all risks are identified and addressed.
Even when the most advanced modeling software tools are used (which allow for thousands of lines of inputs), there is still a great deal that is subject to interpretation. If the practitioner does not possess the expertise or technical ability needed to understand the model, the margin for error can increase substantially. Ultimately, this can lead to overpaying for insurance. Worse, you may end up with a policy with insufficient coverage. In both cases, the profitability of the asset is impacted.
Supplementing CAT studies
In certain instances, it may be necessary to supplement CAT models with an even more detailed analysis of the individual property, equipment, policies, and procedures. In this way, an unbundled risk assessment can be developed that is tailored to the project. Supplemental information (site-specific wind speed studies and hydrological studies, structural assessment, flood maps, etc.) can be considered to adjust vulnerability models.
This provides an added layer of assurance that goes beyond the pre-defined asset descriptions in the software used by traditional studies or assessments. By leveraging expert elicitations, onsite investigations, and rigorous engineering-based methods, it is possible to discretely evaluate asset-specific components as part of the typical financial loss estimate study: this includes Normal Expected Loss (NEL), also known as Scenario Expected Loss (SEL); Probable Maximum Loss (PML), also known as Scenario Upper Loss (SUL); and Probabilistic Loss (PL).
Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and consequences can afford project stakeholders unique insights into quantifying and prioritizing risks, as well as identifying proper mitigation recommendations.
Every project is unique
The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters and extreme weather events globally is placing an added burden on the renewable industry, especially when it comes to project risk assessment and mitigation. Insurers have signaled that insurance may no longer be the main basis for transferring risk; traditional risk management, as well as site and technology selection, must be considered by developers, purchasers, and financiers.
As one of the first steps in understanding exposure and the potential capital loss from a given event, CAT studies are becoming an increasingly important piece of the risk management puzzle. Developers should treat them as such by engaging early in the project lifecycle with an independent third-party practitioner with the specialty knowledge, tools, and expertise to properly interpret models and quantify risk.
Hazards and potential losses can vary significantly depending on the project design and the specific location. Every asset should be evaluated rigorously and thoroughly to minimize the margin for error, and maximize profitability over its life.
 Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
ABS Group | www.abs-group.com




.jpg?r=3503)









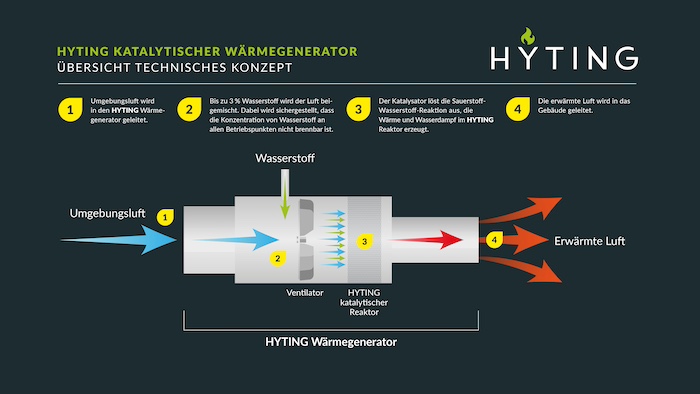
 HYTING’s technology can work alongside heat pumps to form a hybrid and completely CO2-free heating system that can overcome these shortcomings and ensure effective heating under all conditions. This also optimises installation and running costs because the heat pump can be sized at the power rating where it is most energy-efficient, with the HYTING technology supplementing total heating output on cold days and taking care of peak loads. The scalability and flexibility engineered into the technology from day one also means that it can function as a back-up heating source, if needed, or as a standalone system.
HYTING’s technology can work alongside heat pumps to form a hybrid and completely CO2-free heating system that can overcome these shortcomings and ensure effective heating under all conditions. This also optimises installation and running costs because the heat pump can be sized at the power rating where it is most energy-efficient, with the HYTING technology supplementing total heating output on cold days and taking care of peak loads. The scalability and flexibility engineered into the technology from day one also means that it can function as a back-up heating source, if needed, or as a standalone system.














 Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
 Russ is a Director of Product Management, Decision Analytics at Copperleaf. He is an innovative leader with over 20 years of comprehensive business and technical experience in high-tech product development organizations. Russ holds a B.A.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of British Columbia and a Management of Technology MBA from Simon Fraser University.
Russ is a Director of Product Management, Decision Analytics at Copperleaf. He is an innovative leader with over 20 years of comprehensive business and technical experience in high-tech product development organizations. Russ holds a B.A.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from the University of British Columbia and a Management of Technology MBA from Simon Fraser University.